No doubt you have heard of the fancy word ‘Forex’ before, right? What was your first thought about it, have you ever wondered how it works? We are here to give you the proper view and approach on what Forex Trading is and how you can get involved. Our website is the Forex Education 101 – your number one place to improve your knowledge with tons of educational material on how to understand the Forex market from A to Z. Let’s do it!
Forex is an abbreviation for the Foreign Exchange market, or short, the FX. It is the largest financial market in the world.

The foreign exchange can be explained as a network of buyers and sellers. The FX is a global, decentralized market and the place where currencies change hands. If you have ever traveled around the world, you have very likely been involved and made a forex transaction.
History of Forex Trading
Currency trading and exchange first occurred in ancient times. But in its most basic sense, the forex market has been around for hundreds of years. People around the world have always been exchanging their goods and currencies to purchase other goods or services they need.
However, the forex market we know today is a relatively modern invention.
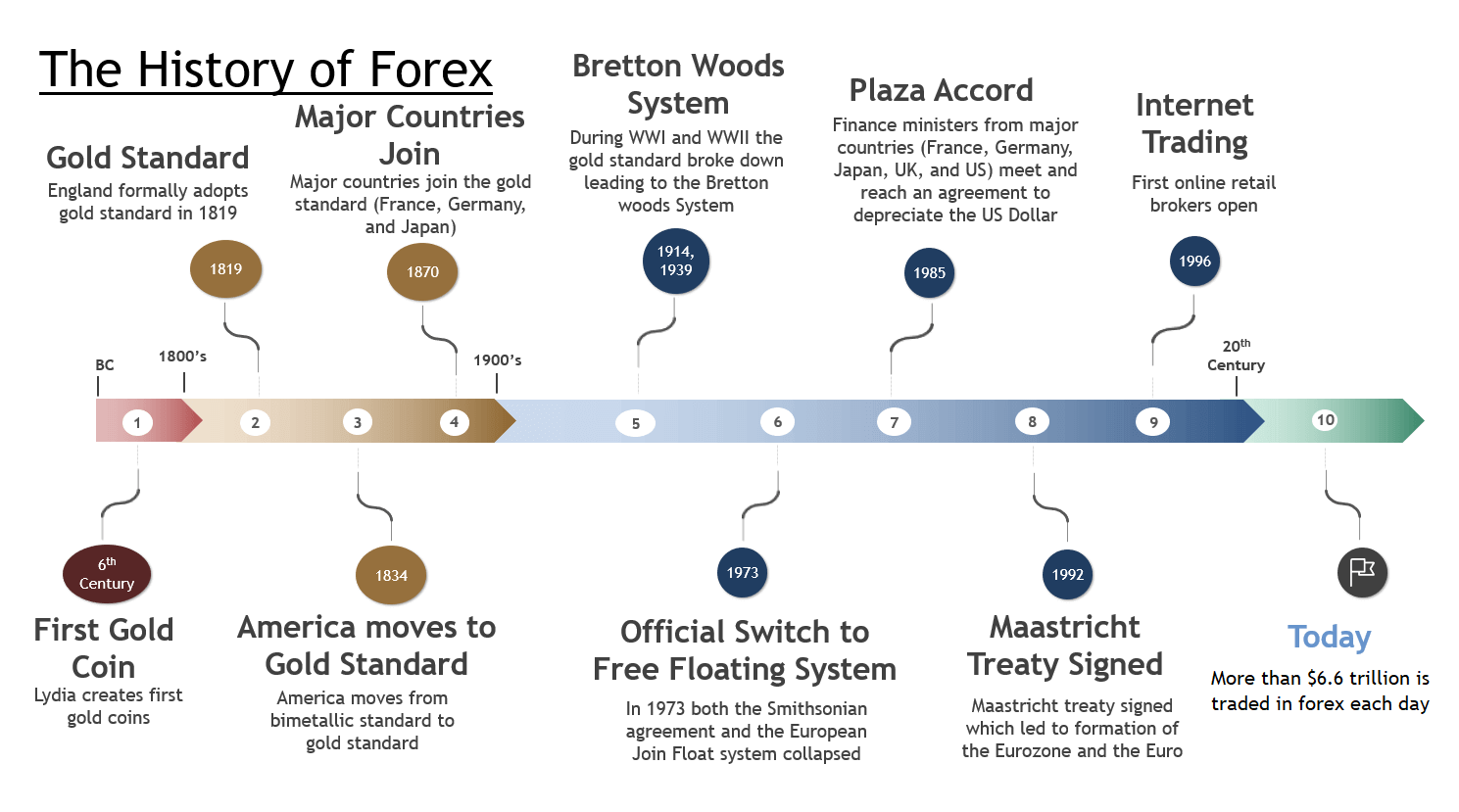
Above: The evolution of Forex Market
The first major transformation of the foreign exchange market, known as the Bretton Woods Accord, occurred at the end of World War II. The United States, Great Britain, and France met at the United Nations Monetary and Financial Conference in Bretton Woods, NH on July 1st, 1944. They met to design a new global economic order.
The Bretton Woods Accord was established to create a stable economic environment, thus the global economies could restore themselves. The Accord attempted this by creating an adjustable pegged foreign exchange market. In other words, this means that exchange rate policy works in the way that a currency is fixed to another currency. In the case of the Bretton Woods Accord, foreign countries would fix their exchange rate to the US Dollar ($).

The Bretton Woods Accord means that there are unified rules and policies set to provide the framework necessary to create fixed international currency exchange rates. Essentially, this agreement was to determine the fixed rate of exchange for currencies around the world. But in 1971, the agreement began to collapse, as the inflationary monetary policy was inappropriate for the key currency country of the system.
So after the 1971’s Bretton Woods accord collapse, more currencies were allowed to float freely against one another on the forex market. The values of each individual currency always vary based on demand and circulation. And currency values of the whole market are monitored by foreign exchange trading services.
Forex Market Trading
Most trading in forex markets is done by the commercial and investment banks, mainly on behalf of their clients. But indeed, there are also speculative opportunities for trading one currency against another for both professional and individual investors. This means that individuals, companies, and central banks convert one currency into another, so they transfer currency between each other at an agreed price.

The goal of the foreign exchange is to make a profit off the changes in the currency value. As the FX market is the biggest market in the world by far, even larger than the stock market or any other, there is huge liquidity involved. The foreign exchange market is attractive for traders around the world, basically from the very beginners to the more experienced.
The FX’s exchange rates change every second, so the market is constantly in flux with currency prices moving up and down.
The Forex market is, compared to the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) daily trading volume of $22.4 billion, a really huge market. Its average daily traded volume is an astonishing 6.6 trillion US dollars, nearly 300 times more. Yes, you have read that absolutely right, a value that is hard to imagine.

6.6 trillion dollars are traded every day. That is 6.600 billion US dollars or 6.600.000 million dollars.
This huge $6.6 trillion number covers the entire global foreign exchange market. However, the most relevant part of the currency market is a so-called ‘spot market‘. This is the place where most forex traders are making transactions. Its size is about one-third (1/3) of the whole FX market, around $2 trillion per day.
And then, you can think of the daily trading volume of us, the individuals – the retail forex traders. It is much, much smaller and is estimated to be around 3-5% of overall daily FX trading volumes. So around $200-300 billion every day.
The vast majority of currency conversion is undertaken with the aim of earning a profit with the exchange. With such an amount of currency converted every single day, we can understand that the price movement of some currencies become very volatile. Thus, it is this exact volatility that makes forex trading so attractive to traders. Traders can earn the interest rate differential between two currencies or they can profit from changes in the exchange rate.
FX trading brings a greater chance of high profits, but it also increases the risk of high losses. This is because the forex market uses high leverage to enhance profit and loss margins with respect to the account size.
The Forex Market is open 24/5
As we have learned, with approximately 6.6 trillion US dollars traded in the forex every day, the market has the highest liquidity in the world. This simply means that we can buy almost any currency we want in high volumes any time the market is open. The advantage of the forex market is that it is open 24 hours a day, five days a week, from Monday to Friday.
Forex trading begins with the opening of the market in Australia, followed by Asia, and then Europe. At last, it is followed by the US market until the markets close on Friday. The markets are only closing down during the weekend. However, the only market that remains open on the weekend is the cryptocurrency market.
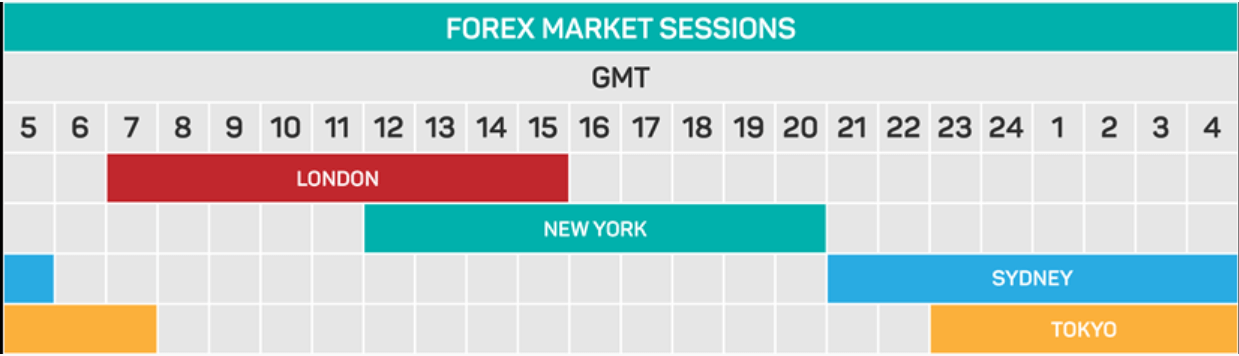
The forex market opening time during the summer is on Sunday at 9:00 pm GMT (or 21 UTC – Coordinated Universal Time), and ends at 9:00 pm GMT (21 UTC) on Friday. In the winter, forex works from Sunday, 10:00 pm GMT to Friday, 10:00 pm GMT, accordingly. This gives a chance for currencies to be traded at all times, day or night. Unlike in other markets, you can always find buyers and sellers in the forex market.
How does the currency market work?
Forex trading is, unlike shares or commodities, working a bit differently. It doesn’t take place on exchanges but it works directly between two parties, in a so-called OTC (Over-The-Counter) market. The OTC is a decentralized market in which market participants trade stocks, commodities, currencies, or other instruments directly between two parties and without a central exchange or a broker.
The forex market is run by a global network of banks, spread across four major forex trading centers in different time zones: London, New York, Sydney, and Tokyo. And there are three different types of forex market:
Spot forex market
Spot Forex Market is the physical exchange of any currency pair. It takes place at the exact point the trade is settled ‘on the spot’ or within a short period of time.
Forward forex market
In the Forward Forex Market, a contract is agreed to buy or sell a set amount of a currency at a specified price. A contract is to be settled at a set date in the future or within a range of future dates.
Future forex market
In the Future Forex Market, a contract is agreed to buy or sell a set amount of a given currency at a set price and date in the future. But unlike forwards, a futures contract is legally binding.
Most of the forex traders that are speculating on prices will not plan to take delivery of the currency itself, but they make exchange rate predictions to take advantage of price movements in the market instead.
Currency Pairs – What is a base and quote currency?
Currency symbols have three letters, the first two letters identify the name of the country and the last, third letter identifies the name of that country’s currency. With the USD for instance, US stands for the United States, D stands for dollar.
With hundreds of currencies around the world, there is always one leading as a ‘master currency’, and the other is acting like a ‘slave currency’.

The first currency listed in a specific forex pair is called a base currency, while the second currency is called the quote currency. So forex trading always involves selling one currency in order to buy the other, that is why it is quoted in pairs. The price of a forex pair tells us how much one unit of the base currency is worth in the quote currency.
With all the currencies in the world, each one has its own three-letter symbol. They are divided into two main categories:
- Major currencies (the Majors)
- Minor currencies (the Minors)
For instance, the major currencies are the following: American (United States) Dollar is represented by the abbreviation symbol USD, Canadian Dollar is CAD, Australian Dollar is (AUD), European Euro is EUR, Swiss Franc is CHF, and British Pound is GBP.

The major currencies are derived from the most powerful economies around the globe, so the US economy, followed by Japan, the main Eurozone, the UK, then Canada, Australia, Switzerland, and New Zealand. When you put them against a counterpart currency, they become a currency pair.
Putting them together as an example, the GBP against the USD becomes GBP/USD where one currency is relative to the other. If the GBP goes down against the USD, then the USD goes up, and vice versa.
So besides the major currencies, the most active crosses are derived from the three major non-US dollar currencies (such as the EUR, AUD, GBP, and YEN). These currency pairs are also known as minors. For example EUR/GBP (Euro Zone/United Kingdom), EUR/AUD (Euro Zone/Australia), GBP/JPY (the United Kingdom/Japan), AUD/JPY (Australia/Japan), etc.
What affects the Forex Trading Market?
As we learned, the huge forex market has very high liquidity, which is due to an elevated supply and demand rate. Global traders apply transactions based on financial events, as well as general economic events. Typically, when a specific currency will be in high demand, its value will raise compared to the other currencies and indeed the opposite.
Mostly every week, economies around the world release statements that are known as financial events. Those are data releases made by countries, central banks, or other financial institutions with involved topics such as the unemployment rate, inflation rate, manufacturing numbers, consumer spending, etc.
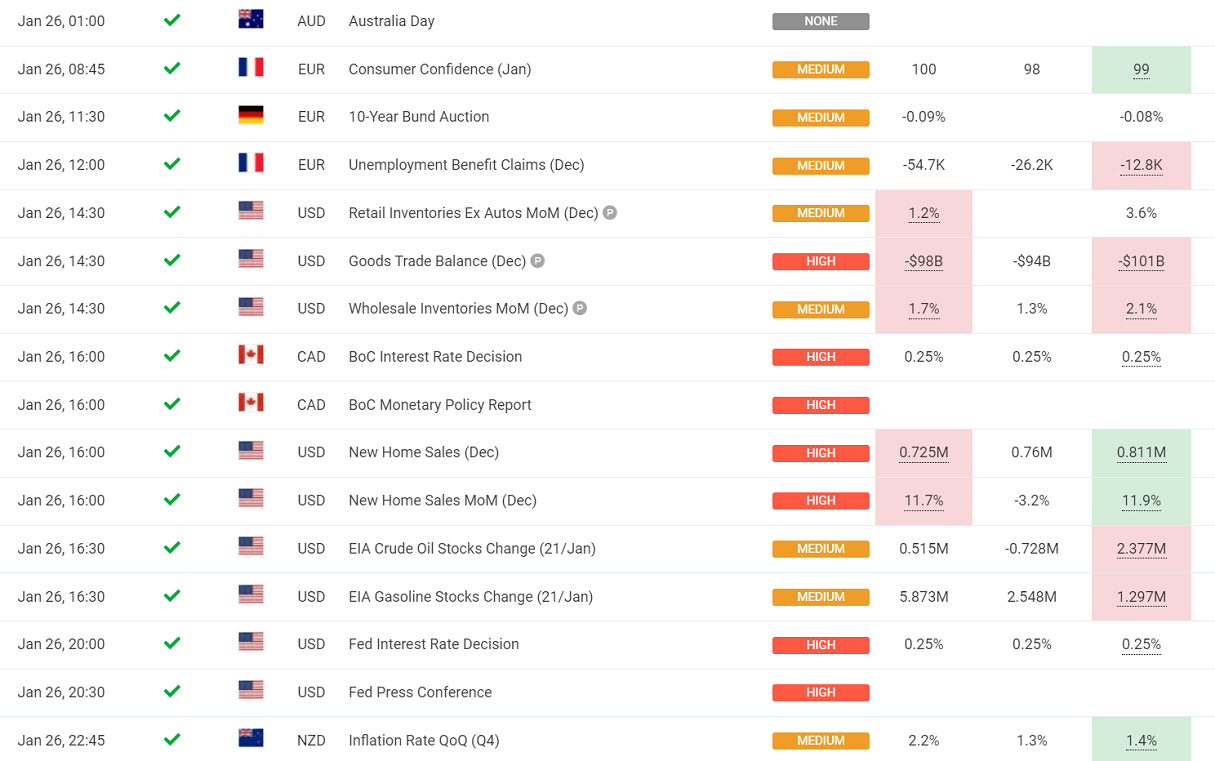
Above: A typical economic calendar report
Before the official numbers are being released, investors release their anticipated figures and expectations.
If the release exceeds expectations, this leads to more volatility in the market and can push the price up of the relevant assets. However, if the release falls below expectation, then the result is the drop-down in the price of the asset lined to the data.
For instance, smaller figures in a country’s unemployment rate usually indicate that its economy of it is strong. Thus it can lead to an increase in the local currency. If that is the base currency, it shoots up against other currencies.
When economic data have a strong effect on the major currencies like USD, EUR, or CAD, it will affect other currencies with the high volatility of their pairs. It is often like that that prior to the economic figures are being released, forex traders speculate on its content, and they open long (buy) or short (sell) positions based on these speculations.
All the events happening abroad are publicly seen and can be followed on the economic calendar.